Description
Slab design analysis involves determining the appropriate dimensions, reinforcement, and structural requirements for a slab, which is a flat, horizontal structural element typically used in buildings and bridges. The analysis ensures that the slab can safely support the applied loads and meet the specified design criteria. Here are the key steps involved in slab design analysis:
- Load Calculation:
- Identify and calculate the various loads acting on the slab, including dead loads (permanent loads like the weight of the structure itself), live loads (variable loads from occupants, furniture, etc.), and other applicable loads.
- Support Conditions:
- Determine the support conditions for the slab, such as whether it is simply supported, continuous, or cantilevered. The support conditions affect the distribution of loads and influence the slab’s design.
- Material Properties:
- Obtain material properties such as the concrete strength, reinforcement yield strength, and other relevant material characteristics. These properties are crucial for performing structural analysis and designing the slab.
- Structural Analysis:
- Conduct a structural analysis of the slab using appropriate methods, such as finite element analysis (FEA), manual calculations, or software tools. This analysis helps determine the internal forces, moments, and deformations within the slab under the applied loads.
- Slab Thickness Design:
- Based on the analysis results, determine the required thickness of the slab. The thickness is influenced by factors like span length, load magnitude, and support conditions.
- Reinforcement Design:
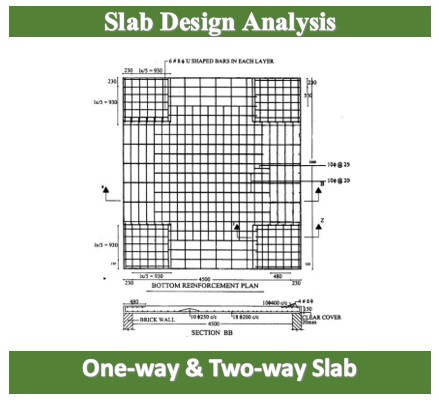
- Calculate and design the reinforcement required to resist tensile forces in the slab. This involves determining the spacing, diameter, and layout of reinforcing bars (rebars) to ensure the slab’s strength and ductility.
- Deflection Control:
- Check and control deflections to ensure that they meet serviceability criteria. Excessive deflections can affect the performance and appearance of the structure.
- Shear and Moment Distribution:
- Analyze the distribution of shear and moment forces throughout the slab. This is crucial for designing the reinforcement layout and ensuring that the slab can resist applied loads without failure.
- Code Compliance:
- Ensure that the slab design complies with relevant building codes and standards. Different regions and countries may have specific codes governing the design of structural elements.
- Detailing:
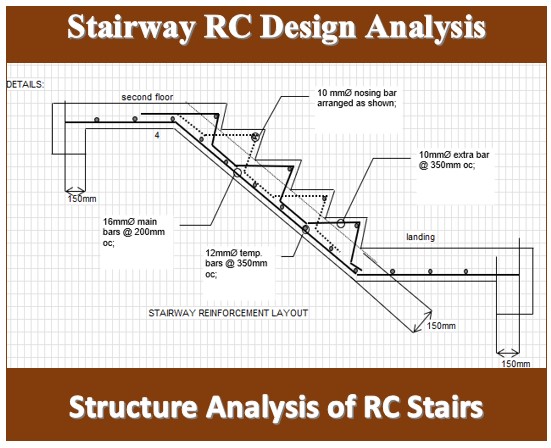
- Provide detailed drawings and specifications for construction, including the layout and detailing of reinforcement, joint locations, and any other relevant information.
It’s important to note that slab design can be a complex process, and consulting with a structural engineer or using specialized structural analysis software is common to ensure accurate and safe results.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.